Bearing capacity online calculator
Problem:
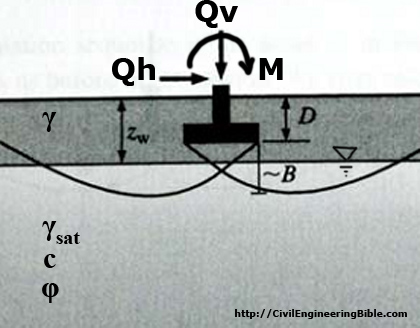
Solution:
Read Meyerhof's bearing capacity theory and formulas here.Factor of Safety against bearing capacity (FS) = 5.3465671261062
Ultimate stress at bearing level (qb) = 891.0945210177 kPa = { Nc term: 0 } + { Nq term: 543.81321558275 } + { Nγ term: 347.28130543495 }
Ultimate Load at bearing level (Qb) = 8019.8506891593 kN
Eccentricity = eB = 0 m
Effective width = B' = B - 2eB = 3 m
Inclination from vertical axis = θ = 0°
Surcharge stress = q0 = 20.38 kPa
Bearing Capacity Factors (N factors): [See formulas]
Nc = 30.139627791519
Nq = 18.401122218709
Nγ = 15.668040821046
Shape factors: [See formulas]
Sc = 1.6
Sq = 1.3
Sγ = 1.3
Depth factors: [See formulas]
dc = 1.2309401076759
dq = 1.1154700538379
dγ = 1.1154700538379
Inclination factors: [See formulas]
ic = 1
iq = 1
iγ = 1
Share this solution with others by sending this link to them:
Hints and Tips on Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundations:
- If there is no water table in the problem use a very large value for "depth of ground water". For instance 9999
- If you are solving a "Strip footing" it is better to use plane-strain friction angle rather than triaxial friction angle
- Meyerhof method does not have "Circular footing" in it, this online calculator uses an equivalent (in terms of area) square footing instead
- If you have layered soil (heterogeneous soil) of the same type (either granular or cohesive) you can use weighted average parameters; for instance if you have n layers of sands with γi and φi, use γ=sum(γi*Hi)/sum(Hi) and φ=sum(φi*Hi)/sum(Hi) where i=1, 2, ..., n
- For rectangular footing if the ratio of L/B>10 you can consider it as strip footing
- Effect of Ground Water Table on bearing capacity of shallow foundations
About Bearing Capacity of Soils:
In geotechnical engineering, bearing capacity is the capacity of soil to support the loads applied to the ground. The bearing capacity of soil is the maximum average contact pressure between the foundation and the soil which should not produce shear failure in the soil. Ultimate bearing capacity (qf) is the theoretical maximum pressure which can be supported without failure; allowable bearing capacity (qa) is the ultimate bearing capacity divided by a factor of safety. Sometimes, on soft soil sites, large settlements may occur under loaded foundations without actual shear failure occurring; in such cases, the allowable bearing capacity is based on the maximum allowable settlement. There are three modes of failure that limit bearing capacity: general shear failure, local shear failure, and punching shear failure. Read more here...
Have a suggestion? Found a bug? Contact us on facebook.
 Share:
Share:
Follow our official Facebook page (@civilengineeringbible) and Twitter page (@CivilEngBible) and do not miss the best civil engineering tools and articles!

