All Types of Foundation Materials
Courses > Construction > Elements of construction > All Types of Foundation Materials Introduction
Introduction
The foundation material should be at least as durable as the rest of the structure. Foundations are subject to attack by moisture, rodents, termites and, to a limited extent, wind. The moisture may come from rain, surface water or groundwater and, although a footing drain can reduce the problem, it is important to use a foundation material that will not be damaged by water or the lateral force created by saturated soil on the outside of the wall.
In some cases the foundation must be watertight in order to prevent water from penetrating into a basement or up through the foundation and into the building walls above. Any foundation should be continued for at least 150 mm above ground level to give adequate protection to the base of the wall from moisture, surface water, etc.
Common materials used in foundations are:
- Stones
- Earth
- Poured concrete
- Concrete blocks
- Bricks
 Concepts and Formulas
Concepts and Formulas
Stones:
Stones are strong, durable and economical to use if they are available near the building site. Stones are suitable for low piers and curtain walls, where they may be laid up without mortar if economy is a major factor, although it is difficult to make them watertight, even if laid with mortar. Also, it is difficult to exclude termites from buildings with stone foundations because of the numerous passages between the stones. However, laying the top course or two in good, rich mortar and installing termite shields can overcome the termite problem to a large degree.
Earth:
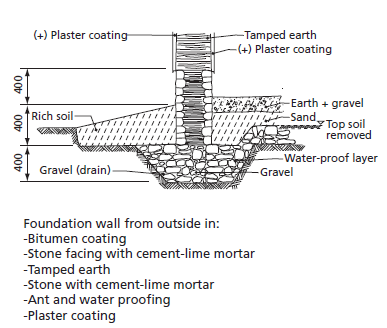
The primary advantage of using earth as a foundation material is its low cost and availability. It is suitable only in very dry climates. Where rainfall and soil moisture are too high for an unprotected earth foundation, they may be faced with stones, as shown in Figure below, or shielded from moisture with polythene sheet.
Poured concrete:
Concrete is one of the best foundation materials because it is hard, durable and strong in compression. It is not damaged by moisture and can be made nearly watertight for basement walls. It is easy to cast into the unique shapes required for each foundation.
For example, curtain walls can be cast in a narrow trench with very little formwork required. The principle disadvantage is the relatively high cost of the cement required to make the concrete.
Concrete blocks:
Concrete blocks may be used to construct attractive and durable foundation walls. The forms required for poured-concrete walls are unnecessary and, because of their large size, concrete blocks will lay up faster than bricks. A block wall is more difficult to make watertight than a concrete wall and does not resist lateral forces as well as a poured-concrete wall.
Bricks:
Stabilized earth bricks or blocks have the same inherent restrictions as monolithic earth foundations. They are suitable only in very dry areas and even there they need protection from moisture. Adobe bricks are too easily damaged by water or ground moisture to be used for foundations. Locally made burnt bricks can often be obtained at low cost, but only the best quality bricks are satisfactory for use in moist conditions. Factorymade bricks are generally too expensive to be used for foundations.
 Watch Videos
Watch Videos
 Solved sample problems
Solved sample problems
 Download Files
Download Files
 Read also
Read also
- Types of Foundations From Construction Point of View
- Factors to consider in foundation design
- Suspension Bridges: Pros and cons along with structural parts details
- Shaft Resistance of Piles
- Grouting: Things a Civil Engineering must know about grouting
 Share
Share
Follow our official Facebook page (@civilengineeringbible) and Twitter page (@CivilEngBible) and do not miss the best civil engineering tools and articles!

